

One distinguishing characteristic of NTFS, compared with FAT, is that it allows for file permissions and encryption. NTFS looks for a storage space that will hold all the clusters of the file, but it isn't always able to find one space all together.Īlong with its data content, each file contains its metadata, which is a description of its attributes. The record is used to locate a file's possibly scattered clusters. When a file is created using NTFS, a record about the file is created in the Master File Table (MFT). With NTFS, generally, the larger the drive, the larger the default cluster size, because it's assumed that a system user will prefer to have fewer disk accesses and better performance at the expense of less efficient use of space. The clusters are indivisible, so even the smallest file takes up one cluster, and a 4.1 KB file takes up two clusters, or 8 KB, on a 4 KB cluster system.Ĭluster sizes are determined based on balancing a tradeoff between maximizing use of disk space and minimizing the number of disk accesses required to get a file. For example, a 4 gigabyte (GB) drive has a default cluster size of 4 KB.
CAN I USE NTFS ON MAC WINDOWS
Windows NT provides a recommended default cluster size for each drive size. Using NTFS, the sizes of the clusters range from 512 bytes to 64 KB. Each file is stored on the HDD in one or more cluster s or disk spaces of a predefined uniform size. Within each partition, the OS keeps track of all the files it stores. Partitions are the major divisions of the hard drive's physical space. When an HDD is formatted or initialized, it is divided into partitions.

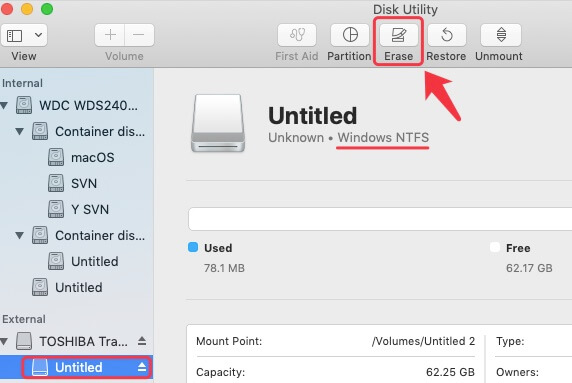
The process of formatting each type of drive is slightly different, but both are compatible with NTFS. When formatting an SSD or an HDD, users choose the file system they'll use. When installing an OS, the user chooses a file system. The theoretical limit for the individual file size NTFS can support is 16 exbibytes minus 1 kilobyte (KB). NTFS can support up to 8 petabyte volumes and files on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10, according to Microsoft. NTFS is also used on external drives because it has the capacity those drives need, supporting large files and partition sizes.
CAN I USE NTFS ON MAC MAC
On the other hand, FAT32 and exFAT work better with non-Windows OSes, such as Mac and Linux.Īll Microsoft OSes from Windows XP on use NTFS version 3.1 as their main file system. For example, security and permissions are more advanced with NTFS than exFAT and FAT32. Each file system has benefits and drawbacks. NTFS is an option for formatting SSDs - where its speed is particularly useful - HDDs, USBs and micro SD cards that are used with Windows.ĭepending on the storage capacity of the device, the OS used and the type of drive, a different file system may be preferable, such as FAT32 or Extended FAT (exFAT). Microsoft Windows and some removable storage devices use NTFS to organize, name and store files. A DFS enables multiple users to easily share data and files on a network and provides redundancy. Today, there is also a distributed file system (DFS) where files are stored across multiple servers but is accessed and handled as if it were stored locally. File systems are generally differentiated by the OS and the type of drive they are being used with. It controls how data files are named, stored, retrieved and updated and what other information can be associated with the files - for example, data on file ownership and user permissions. The file system essentially organizes the data into files. However, NTFS offers several improvements over FAT and HPFS in terms of performance, extendibility and security.Ī computer's OS creates and maintains the file system on a storage drive or device. NTFS is the Windows NT equivalent of the Windows 95 file allocation table ( FAT) and the OS/2 High Performance File System (HPFS). NTFS, which stands for NT file system and the New Technology File System, is the file system that the Windows NT operating system (OS) uses for storing and retrieving files on hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
